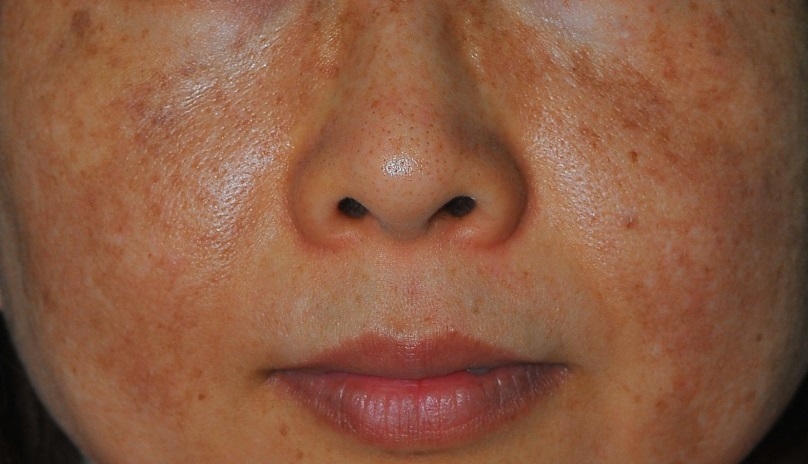
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by brown or gray patches on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. While there is no known cure for melasma, several treatment options can help manage and reduce its appearance.
The exact cause of melasma is not fully understood, but there are several factors that contribute to its development. These include:
-
- Sun Exposure: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun is considered the primary trigger for melasma. UV rays stimulate the production of melanin (the pigment responsible for skin color), leading to the formation of dark patches. Sun exposure can worsen existing melasma and increase the risk of developing new patches.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, play a significant role in melasma. It is commonly observed during pregnancy (referred to as “pregnancy mask” or chloasma) due to hormonal changes, but it can also occur due to hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
- Genetic Predisposition: There appears to be a genetic component to melasma, as it often runs in families. If your close relatives have melasma, you may be more prone to developing it as well.
- Ethnicity: Melasma is more common in individuals with darker skin types, including those of Asian, Hispanic, African, and Middle Eastern descent. People with higher levels of melanin in their skin are more susceptible to melasma.
- Other Triggers: Certain medications, cosmetics, and skin care products containing irritating ingredients or allergens can trigger or worsen melasma in some individuals. Additionally, heat, stress, and thyroid disorders have been associated with melasma development in some cases.
It’s important to note that the exact cause and triggers of melasma can vary from person to person. Understanding these factors can help in managing and preventing melasma effectively. For those prone to melasma, diligent sun protection and avoidance of known triggers are key strategies to reduce the risk of developing or worsening melasma patches.
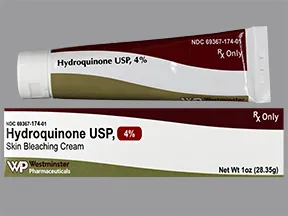
Here are some common approaches to melasma treatment:
-
- Topical Creams: Prescription creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, tretinoin, corticosteroids, or azelaic acid can be effective in lightening the dark patches of melasma. These creams are typically applied to the affected areas as directed by a dermatologist.
- Chemical Peels: Dermatologists may recommend chemical peels, which involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin to exfoliate and remove the top layer. This helps to lighten the melasma patches gradually. Superficial peels using mild acids like glycolic acid or salicylic acid are commonly used for melasma treatment.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-536778385-a8e9aef3c05f492aba53a9767a2d0c6e.jpg)
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can target the deeper layers of the skin to break up the excess melanin responsible for melasma. Different types of lasers, such as Q-switched Nd:YAG or fractional lasers, may be used based on the severity of the condition. Multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): IPL treatment uses broad-spectrum light to target melanin and break up pigmented areas. It can help lighten melasma patches and even out skin tone. Similar to laser therapy, multiple sessions may be needed for desired outcomes.
- Sun Protection: Protecting the skin from the sun is crucial for melasma management. Sunscreen with a high SPF (30 or above) and broad-spectrum protection should be applied daily, even on cloudy days. Wearing wide-brimmed hats, using protective clothing, and avoiding direct sun exposure during peak hours can also help prevent melasma from worsening.
It’s important to consult a dermatologist or skin care specialist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan for melasma. They can assess the severity of your condition and recommend the most suitable treatment options for you. Additionally, it’s worth noting that melasma may recur even after successful treatment, so long-term management and sun protection are essential for maintaining results.




