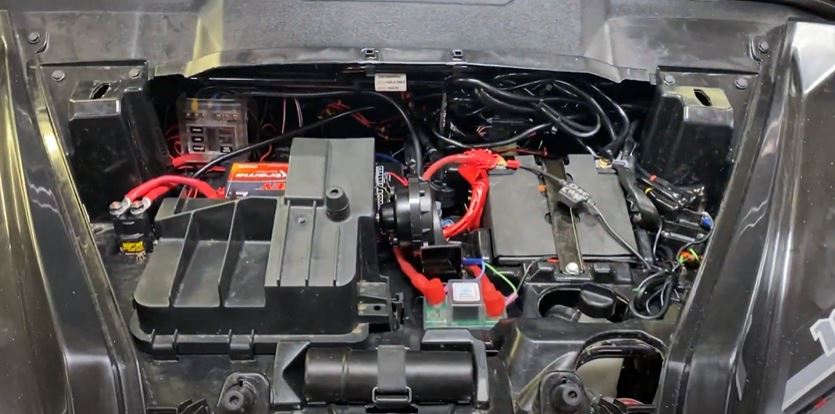
Testing a dual battery isolator helps ensure that it is functioning correctly and efficiently. Here’s a general guide on how to test a dual battery isolator:
- Start with a fully charged battery: Ensure that both the primary (main) battery and the secondary (auxiliary) battery are fully charged before beginning the test.
- Disconnect power sources: Disconnect any power sources, such as solar panels or chargers, from both batteries to isolate the batteries from external influences during the test.
- Check battery voltage: Use a multimeter or voltmeter to measure the voltage of each battery individually. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 to 12.8 volts. If either battery has a significantly lower voltage, it may indicate a problem with the battery itself.
- Connect the isolator: If your dual battery isolator has an override switch, ensure it is in the correct position for testing (usually the “On” or “Normal” position). Connect the isolator as per the manufacturer’s instructions, making sure all connections are secure.
- Monitor voltage during charging: Start the engine of your vehicle and monitor the voltage of both batteries while the engine is running. The primary battery voltage should rise, indicating that it is being charged by the alternator. The secondary battery voltage should remain relatively stable or increase slightly as well.
- Check isolator operation: With the engine running, turn on any high-power electrical accessories in your vehicle, such as headlights, air conditioning, or audio system. Monitor the voltage of both batteries to ensure that the primary battery voltage remains stable and the secondary battery voltage does not drop significantly.
- Test battery separation: Turn off the engine and any electrical accessories. Leave the primary battery connected and disconnect the secondary battery from the isolator. Measure the voltage of each battery separately. The primary battery voltage should remain stable, while the secondary battery voltage should be disconnected and should not show any voltage.
- Test battery charging: Reconnect the secondary battery to the isolator and start the engine again. Monitor the voltage of both batteries to ensure that the primary battery voltage rises, indicating charging, while the secondary battery voltage remains relatively stable or increases slightly.
If during the testing process you notice any significant voltage drops, inconsistencies, or other irregularities, it may indicate a problem with the dual battery isolator or the batteries themselves. In such cases, it’s advisable to consult the manufacturer’s instructions or seek professional assistance to diagnose and address the issue.




